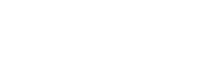Solar farms

Fugitive dust emissions pose a significant challenge to the efficiency of solar and wind installations. For solar panels, particularly bifacial ones, dust can block radiation on both the front and rear surfaces, drastically reducing energy generation. For wind turbines, the accumulation of particles on components can impair performance and accelerate wear.
ABCDust provides sustainable and intelligent solutions for dust control and soil stabilization in these installations, to enhance their efficiency, durability, and environmental sustainability.
Benefits of Dust Control and Soil Stabilization
Challenges of Traditional Methods and Advantages of ABCDust Solutions
-
Limitations of Traditional Methods:
Methods such as water-based cleaning or using harmful chemicals are unsustainable in the long term. Water consumption is inefficient and costly, while certain chemicals can damage the environment and equipment. -
Advantages of ABCDust Solutions:
- Reduces dust by up to 98%.
- Eco-friendly, non-toxic, water-resistant, and UV-resistant products.
- Compatible with heavy traffic and extreme weather conditions.
- Solutions tailored to the specific needs of each project.
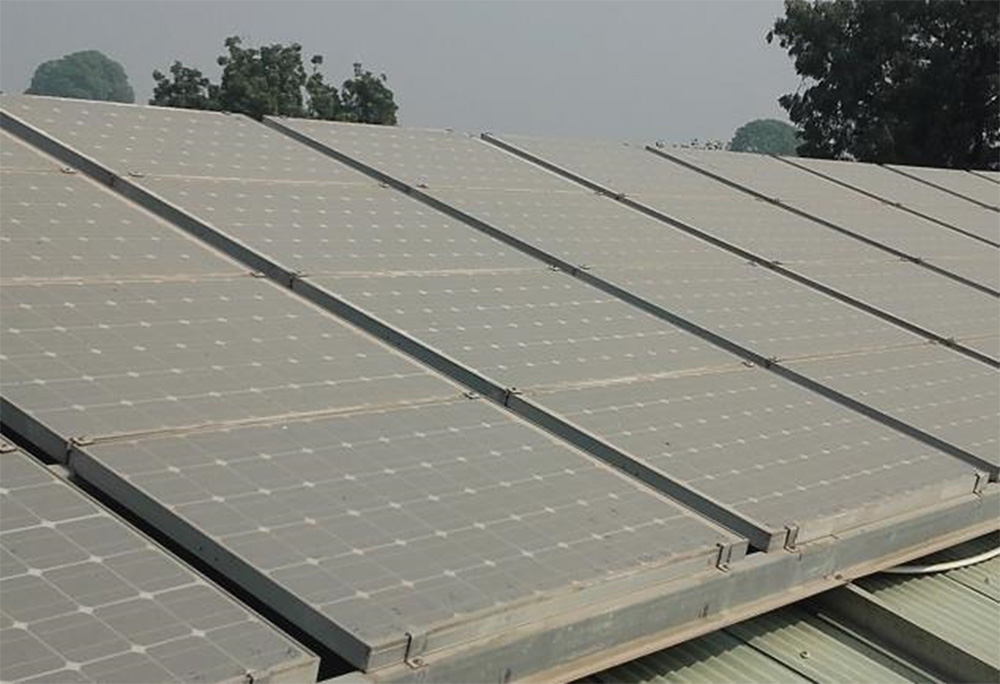

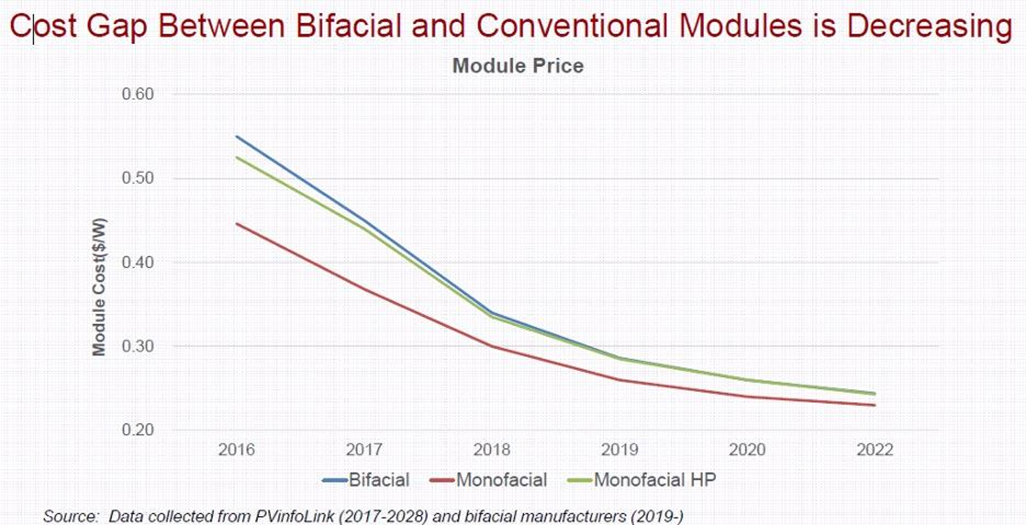
Combining Bifacial Solar Energy with Dust Control
ABCDust has developed additives for dust control with an ideal albedo factor for bifacial farms applied to the top layer of the solar farm. These solutions can be combined with ABCDust’s soil stabilization products to stabilize the soil of the solar farm, mitigate dust issues, and maximize its albedo factor. ABCDust’s DMS-ALB® additive significantly reduces dust accumulation on solar panels and maximizes the efficiency of bifacial solar panels, helping solar farms produce clean energy and reduce CO₂ emissions.
Let’s decarbonize the world and power the grid with more efficient clean solar energy.